- Mon - Sat : 5:30 - 8:30
- Sunday - CLOSED
- +91 99304 53556
- drshridhargpadagatti@gmail.com
- Khar(W), Mumbai
- 001, Himath Ghar
- admindrshridhar
- 0 Comments
Do You Know The 4 Heart Valves & Their Functions?
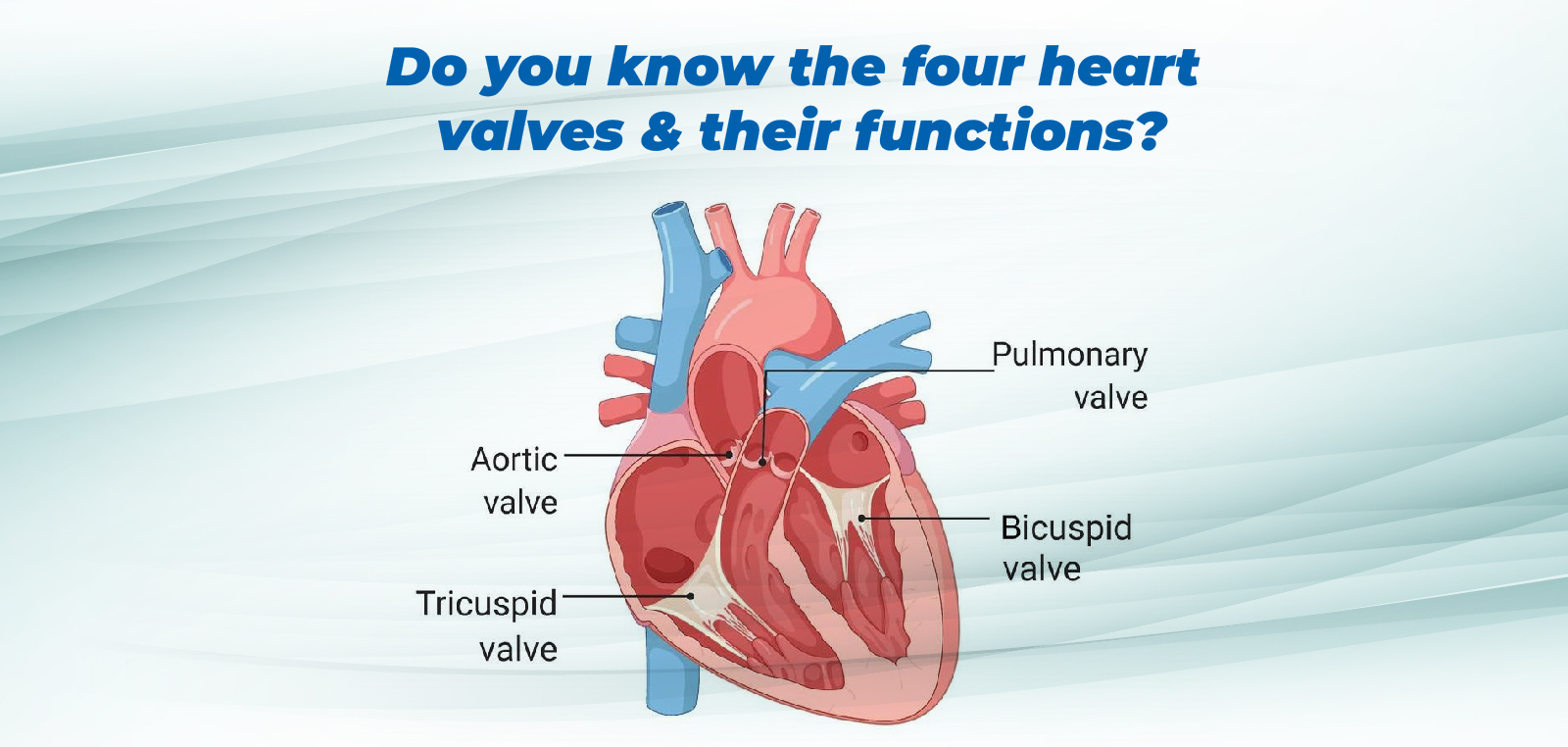
Do You Know The 4 Heart Valves & Their Functions? and Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Cost ? What Are the 4 Heart Valves and Their Functions? The heart, a vital organ, functions as a pump to circulate blood throughout the body. It comprises four chambers: two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). Blood flows through a valve before leaving each chamber of the heart, ensuring unidirectional blood flow and preventing backflow. The four heart valves are: Tricuspid Valve: Located between the right atrium and the right ventricle, it prevents the backflow of blood into the right atrium when the right ventricle contracts. Pulmonary Valve: Situated between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, it ensures blood flows from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery, preventing backflow. Mitral Valve: Located between the left atrium and the left ventricle, it has only two leaflets (flaps). It allows blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle and prevents backflow during ventricular contraction. Aortic Valve: Positioned between the left ventricle and the aorta, it ensures blood flows from the left ventricle into the aorta and prevents backflow. How Do the Heart Valves Work? As the heart muscle contracts and relaxes, the valves open and close, allowing blood to flow into the ventricles and atria alternately. Here is a step-by-step description of how the valves function: Left Ventricle Relaxation: The aortic valve closes, and the mitral valve opens, allowing blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Left Atrium Contraction: Additional blood flows into the left ventricle. Left Ventricle Contraction: The mitral valve closes, and the aortic valve opens, allowing blood to flow into the aorta and out to the body. Right Ventricle Relaxation and Contraction: Simultaneously with the left ventricle, the right ventricle relaxes and contracts, allowing blood flow into the pulmonary artery and preventing backflow into the right atrium. What Is Heart Valve Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when one or more valves in the heart do not function correctly. The main types of heart valve diseases include: Regurgitation: Also known as a leaky valve, it occurs when a valve does not close properly, causing blood to flow backward. This can lead to overworking of the heart chambers, potentially causing structural changes. Stenosis: This is a condition where the valve opening is narrowed, making it difficult for blood to pass through. The heart must exert more force to pump blood, which can also lead to structural changes. Atresia: This is a congenital condition where a valve does not develop properly, preventing blood flow through the heart. When heart valves do not open or close properly, it can seriously affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. What Is Heart Valve Replacement Surgery? Heart valve replacement surgery is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased heart valves. The surgery is performed when valves are severely damaged, affecting blood flow through the heart. There are two main types of valves used in replacement surgeries: Mechanical Valves: Made from durable materials like plastic, carbon, or metal, these valves can last for many years. However, patients with mechanical valves need to take blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants) for life to prevent blood clots. Biological Valves: Made from animal tissue (xenograft) or donated human tissue (allograft or homograft), these valves do not require lifelong blood-thinning medications. However, they may need to be replaced every 10-15 years. Types of Heart Valve Replacement Procedures Open Heart Surgery: This traditional method involves a large incision in the chest to access the heart and replace the valve. Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery: This method involves smaller incisions and specialized instruments to replace the valve, leading to a quicker recovery. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR): A minimally invasive procedure performed for patients who are not suitable for open-heart surgery. It involves threading a catheter through a blood vessel to replace the aortic valve. Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Cost The cost of heart valve replacement surgery can vary depending on several factors, including the type of valve used, the complexity of the procedure, and the hospital. In India, the average cost of TAVR or heart valve replacement surgery ranges from Rs. 3,00,000 to Rs. 5,00,000. Costs may vary based on the hospital and city. Why Heart Valve Replacement Surgery is Necessary? Heart valve replacement surgery is essential for patients with severe heart valve disease. It can significantly improve the quality of life by restoring normal blood flow through the heart and reducing symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Depending on the severity of the valve damage, the patient’s age, and overall health, the surgeon will recommend the most appropriate type of valve and surgical procedure. Conclusion: Understanding the function of the heart valves and the importance of heart valve replacement surgery is crucial for maintaining heart health. If you experience symptoms of heart valve disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue, consult a cardiac specialist like Dr. Shridhar G. Padagatti at Active Heart Clinic. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve your quality of life. With advancements in medical technology, heart valve replacement surgery has become safer and more effective, offering patients a new lease on life.
- admindrshridhar
- 0 Comments
Cost of open heart surgery in india
Cost of Open Heart Surgery in India Open heart surgery is a critical and often life-saving procedure that many patients with severe heart conditions may need to undergo. However, one of the significant concerns for patients and their families is the cost associated with such an extensive surgical procedure. This blog aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the cost of open heart surgery in India, with a particular focus on the expertise available at Active Heart Clinic, led by Dr. Shridhar G Padagatti. About Active Heart Clinic and Dr. Shridhar G Padagatti Active Heart Clinic is renowned for its exceptional cardiac care, led by Dr. Shridhar G Padagatti, a highly respected cardiac and vascular surgeon. Dr. Padagatti has an impressive educational background, beginning with his MBBS from JNMC, Belgaum, affiliated with Karnataka University. He then pursued a specialization in General Surgery, earning his MS degree from Goa Medical College. To further enhance his expertise, he completed a super-specialization in Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery (CVTS) from Seth GS Medical College and KEM Hospital, Mumbai, graduating with this prestigious degree in December 2009. Dr. Padagatti has worked in several reputed hospitals across Mumbai, Maharashtra. His current affiliations include P.D. Hinduja Hospital, Khar (West), Bharatiya Arogya Nidhi Hospital (Juhu), Holy Spirit Hospital (Andheri East), BSES Hospital (Andheri West), Wockhardt Hospital (Mira Road East), and Bhakti Vedanta Hospital (Mira Road East). His extensive experience and dedication to cardiac surgery have made him a trusted name in the field. What is Open Heart Surgery? Open heart surgery is a procedure where the surgeon makes an incision through the breastbone (sternum) to access the heart. This method, often referred to as “chest cracking,” involves spreading the ribs to gain direct access to the heart. It is a traditional and reliable method for performing various heart surgeries, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), heart valve repair or replacement, heart transplantation, and surgery for congenital heart defects. Despite the term “open heart surgery,” many modern heart surgeries can now be performed using minimally invasive techniques, which involve smaller incisions and less recovery time. However, traditional open heart surgery remains a standard approach for many complex heart conditions. Conditions Requiring Open Heart Surgery Several heart conditions may necessitate open heart surgery, including: Congenital heart defects such as atrial septal defect (heart hole) and hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Coronary artery disease which may require CABG to bypass blocked arteries. Heart failure where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively. Heart valve disease requiring repair or replacement of damaged valves. Thoracic aortic aneurysm, a bulging of the aorta that can lead to life-threatening complications. In cases of coronary artery disease, open heart surgery may be needed when the coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This condition restricts blood flow, increasing the risk of a heart attack. Techniques Used in Open Heart Surgery Open heart surgery can be performed using two primary techniques: on-pump and off-pump surgery. On-pump surgery (CPB): This traditional method involves stopping the heart and using a cardiopulmonary bypass machine (heart-lung machine) to maintain blood circulation and oxygenation during the surgery. The machine takes over the heart and lung functions while the surgeon performs the procedure on a non-beating heart. Off-pump surgery: Also known as beating-heart surgery, this technique involves performing the surgery while the heart is still beating. Specialized equipment is used to stabilize the part of the heart being operated on, allowing the rest of the heart to continue pumping blood. This approach eliminates the need for a heart-lung machine and can reduce certain risks associated with stopping the heart. Pre-Surgery Tests Before undergoing open heart surgery, several tests are typically performed to ensure the patient’s suitability for the procedure and to minimize risks. Common pre-surgery tests include: Echocardiogram (Echo): Assesses heart muscle function and valve operation. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Records the heart’s electrical signals to check for abnormalities. Lab tests: Evaluate kidney and liver function, blood count, and other vital parameters. Chest X-ray: Provides images of the heart, lungs, and chest bones. Dobutamine stress echocardiogram (DSE): Mimics exercise effects on the heart using medication. Treadmill test (TMT): Assesses heart function under physical stress. Complete blood count (CBC): Detects disorders like anemia and infection. Cardiac MRI: Offers detailed images of the heart’s internal structures. Angiography: X-ray technique to examine blood vessels and detect blockages. Performing Open Heart Surgery Open heart surgery typically requires a hospital stay of 7-10 days. The procedure involves several steps: Preparation: The patient is placed under general anesthesia. Incision: An 6-8 inch incision is made in the chest. Accessing the Heart: The sternum is cut, and the ribcage is spread to expose the heart. On-Pump or Off-Pump: Depending on the technique, a heart-lung machine may be used. Surgery: The specific surgical procedure is performed. Restoring Heart Function: The heart is restarted, and blood flow is restored. Closing Incisions: The sternum and skin are sutured. Post-Surgery Recovery After surgery, patients spend time in the ICU for close monitoring. Symptoms like pain, swelling, memory issues, and depression are common post-surgery. Follow-up sessions with the doctor are crucial for recovery. Costs of Open Heart Surgery in India The cost of open heart surgery in India varies depending on several factors, including the type of surgery, the hospital, the surgeon’s expertise, and the patient’s overall health. On average, open heart surgery in India can cost between INR 1.5 lakhs to INR 5 lakhs. Specific procedures, like CABG, typically cost around INR 2.75 lakhs. Conclusion: Open heart surgery is a critical procedure that can address severe heart conditions and save lives. Understanding the costs involved and the procedures can help patients and their families make informed decisions. At Active Heart Clinic, Dr. Shridhar G Padagatti offers exceptional expertise and care, ensuring that patients receive the best possible treatment. If you or a loved one needs open heart surgery, do not delay seeking the necessary medical intervention. Your heart health is invaluable, and timely surgery